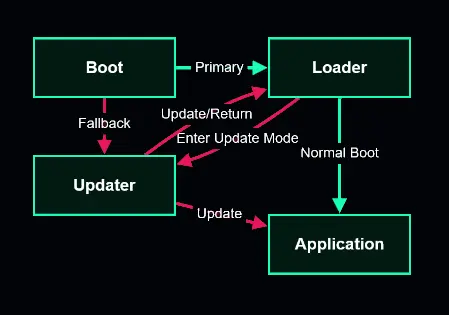
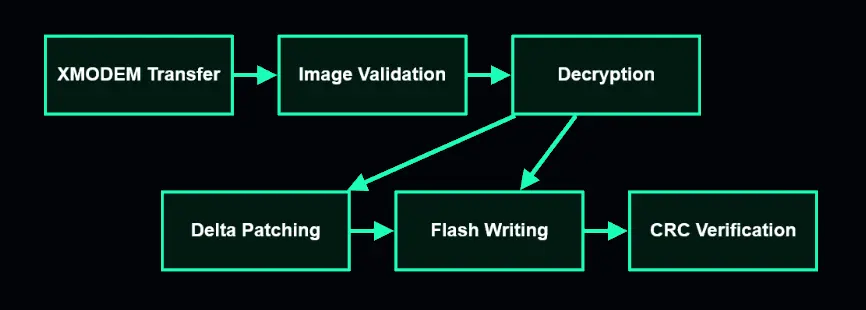
Project Goal: Implement a secure multi-element bootloader that supports encrypted updates and delta patches.
This bootloader delivers AES-128-GCM GMAC encryption while reducing update sizes by up to 90% through delta patching. That means faster updates for smaller chanages and uncompromised security.
The four-stage architecture creates a chain of trust where each component validates the next before executing it. If something goes wrong during an update, the failsafe recovery system automatically restores from backup - so no bricked devices.